TOBACCO is a drug that contains NICOTINE (a stimulant) used in cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing and dipping products and is the world’s #1 greatest cause of preventable disease or death.
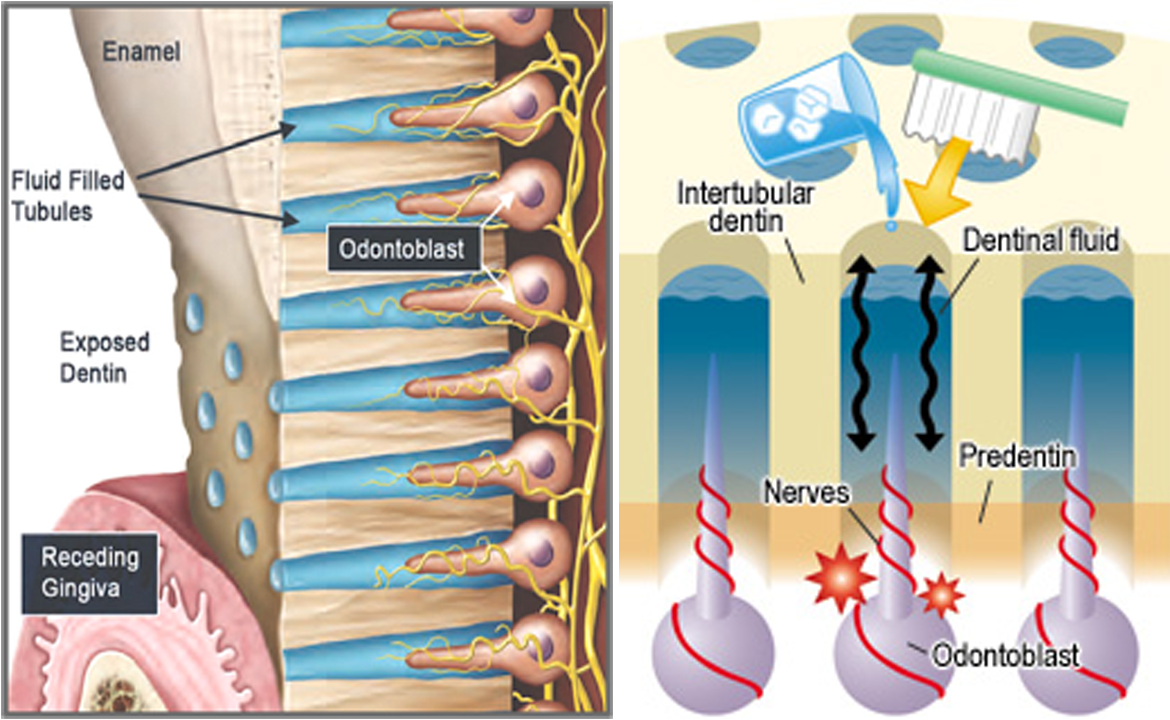
Tobacco increases the risk of lung cancer, COPD, hypertension, heart disease, ORAL & NECK CANCER (squamous cell carcinoma), pancreatic cancer, spontaneous abortion, SIDS, and PERIODONTAL DISEASE (7-10 times greater risk due to reduced vascularity).
SMOKING DECREASES the PLAQUE ACCUMULATION RATE, GINGIVAL VASCULARITY, gingival inflammation and decreases BOP. Smokers are NOT at increased risk for caries (due to the decreased plaque accumulation rate).
In terms of dental management, ALWAYS perform a thorough comprehensive exam due to the increased risk for oral cancer and provide smoking cessation assistance. Apply the “5 A’s” to a smoking cessation program: (1st Ask, 2nd Advise, 3rd Assess, 4th Assist, and 5th Arrange). For more helpful practical NBDE & NBDHE information, please visit dentin.co.